Peer Reviewed Journals
-
Health Affairs: Effects Of State Insurance Mandates On Health Care Use And Spending For Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Read more: Health Affairs: Effects Of State Insurance Mandates On Health Care Use And Spending For Autism Spectrum Disorder
Read more: Health Affairs: Effects Of State Insurance Mandates On Health Care Use And Spending For Autism Spectrum DisorderABSTRACT: Forty-six states and the District of Columbia have enacted insurance mandates that require commercial insurers to cover treatment for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This study examined whether implementing autism mandates altered service use or spending among commercially insured children with ASD. We compared children age twenty-one or younger who were eligible for mandates…
-
JAMA Oncology: Association Between Quality of Care for Breast Cancer and Health Insurance Exchange Coverage An Analysis of Use of Radiation Therapy After Breast-Conserving Surgery
 Read more: JAMA Oncology: Association Between Quality of Care for Breast Cancer and Health Insurance Exchange Coverage An Analysis of Use of Radiation Therapy After Breast-Conserving Surgery
Read more: JAMA Oncology: Association Between Quality of Care for Breast Cancer and Health Insurance Exchange Coverage An Analysis of Use of Radiation Therapy After Breast-Conserving SurgeryABSTRACT Research comparing quality of cancer care by insurance categories concluded that cancer patients without insurance or with Medicaid experienced inferior quality of care compared with those with private insurance. A new insurance category created from the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is insurance purchased from the Health Insurance Marketplace (also known as the exchange). The present…
-
Health Affairs: Insurer Market Power Lowers Prices In Numerous Concentrated Provider Markets
Tags: Health Affairs, Inpatient Spending, Market Concentration, Outpatient Spending, Peer Reviewed Journals Read more: Health Affairs: Insurer Market Power Lowers Prices In Numerous Concentrated Provider Markets
Read more: Health Affairs: Insurer Market Power Lowers Prices In Numerous Concentrated Provider MarketsABSTRACT: Using prices of hospital admissions and visits to five types of physicians, we analyzed how provider and insurer market concentration—as measured by the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI)—interact and are correlated with prices. We found evidence that in the range of the Department of Justice’s and Federal Trade Commission’s definition of a moderately concentrated market (HHI of…
-
NBER: Does Multispecialty Practice Enhance Physician Market Power?
 Read more: NBER: Does Multispecialty Practice Enhance Physician Market Power?
Read more: NBER: Does Multispecialty Practice Enhance Physician Market Power?ABSTRACT: In markets for health services, vertical integration – common ownership of producers of complementary services – may have both pro- and anti-competitive effects. Despite this, no empirical research has examined the consequences of multispecialty physician practice – a common and increasing form of vertical integration – for physician prices. We use data on 40 million…
-
Women’s Health Issues: Maternal Medical Complexity Impact on Prenatal Health Care Spending among Women at Low Risk for Cesarean Section
Tags: Commercially Insured, Inpatient Spending, Maternal Health, Outpatient Spending, Peer Reviewed JournalsRead more: Women’s Health Issues: Maternal Medical Complexity Impact on Prenatal Health Care Spending among Women at Low Risk for Cesarean SectionABSTRACT Background: Obstetric procedures are among the most expensive health care services, yet relatively little is known about health care spending among pregnant women, particularly the commercially-insured. Objective: The objective of this study was to examine the association between maternal medical complexity, as a result of having one or more comorbid conditions, and health care…
-
Academic Emergency Medicine: Association Between Maternal Comorbidities and Emergency Department Use Among a National Sample of Commercially Insured Pregnant Women
Read more: Academic Emergency Medicine: Association Between Maternal Comorbidities and Emergency Department Use Among a National Sample of Commercially Insured Pregnant WomenABSTRACT Objectives: Evidence suggests that, despite routine engagement with the health system, pregnant women commonly seek emergency care. The objectives of this study were to examine the association between maternal comorbidities and emergency department (ED) use among a national sample of commercially insured pregnant women. Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using multipayer medical…
-
Health Affairs: Reference Pricing Changes the ‘Choice Architecture’ of Health Care for Consumers
 Read more: Health Affairs: Reference Pricing Changes the ‘Choice Architecture’ of Health Care for Consumers
Read more: Health Affairs: Reference Pricing Changes the ‘Choice Architecture’ of Health Care for ConsumersABSTRACT: Reference pricing in health insurance creates incentives for patients to select for nonemergency services providers that charge relatively low prices and still offer high quality of care. It changes the “choice architecture” by offering standard coverage if the patient chooses cost-effective providers but requires considerable consumer cost sharing if more expensive alternatives are selected….
-
Health Services Research: Payer Type and Low‐Value Care: Comparing Choosing Wisely Services across Commercial and Medicare Populations
 Read more: Health Services Research: Payer Type and Low‐Value Care: Comparing Choosing Wisely Services across Commercial and Medicare Populations
Read more: Health Services Research: Payer Type and Low‐Value Care: Comparing Choosing Wisely Services across Commercial and Medicare PopulationsABSTRACT Objective: To compare low‐value health service use among commercially insured and Medicare populations and explore the influence of payer type on the provision of low‐value care. Data Sources: 2009–2011 national Medicare and commercial insurance administrative data. Design: We created claims‐based algorithms to measure seven Choosing Wisely‐identified low‐value services and examined the correlation between commercial…
-
JAMA Internal Medicine: A Perspective on Out-of-Pocket Spending
 Read more: JAMA Internal Medicine: A Perspective on Out-of-Pocket Spending
Read more: JAMA Internal Medicine: A Perspective on Out-of-Pocket SpendingTo the Editor Understanding out-of-pocket spending is critical to understanding health care costs in the United States. We applaud the efforts of Adrion et al as an important contribution to understanding the out-of-pocket spending of the commercially insured population younger than 65 years. The commercially insured comprise over 50% of the nonelderly US population and, as…
-
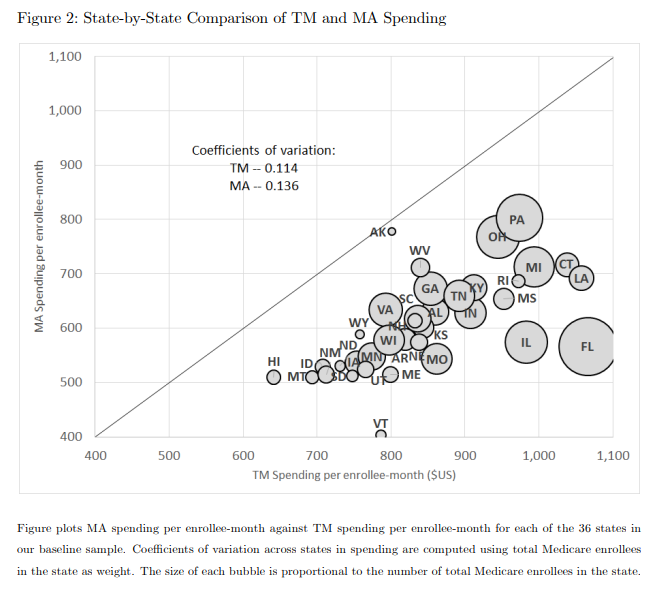
NBER Working Paper: Healthcare Spending and Utilization in Public and Private Medicare
Tags: Geographic Variation, Medicare, Medicare Advantage, NBER, Peer Reviewed Journals, Value Based CareRead more: NBER Working Paper: Healthcare Spending and Utilization in Public and Private MedicareABSTRACT: We compare healthcare spending in public and private Medicare using newly available claims data from Medicare Advantage (MA) insurers. MA insurer revenues are 30 percent higher than their healthcare spending. Healthcare spending is 25 percent lower for MA enrollees than for enrollees in traditional Medicare (TM) in the same county with the same risk…